- Hosts are servers with Agents installed.
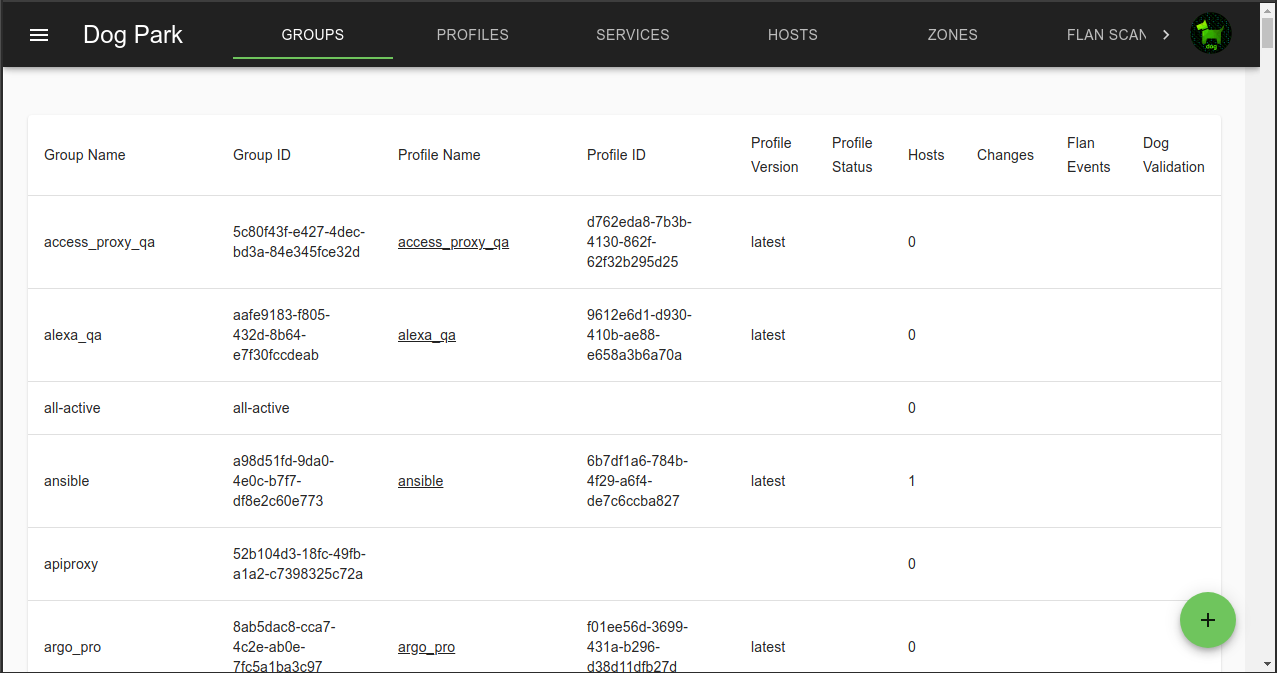
- Groups are collections of Hosts.
- Zones are lists of addresses.
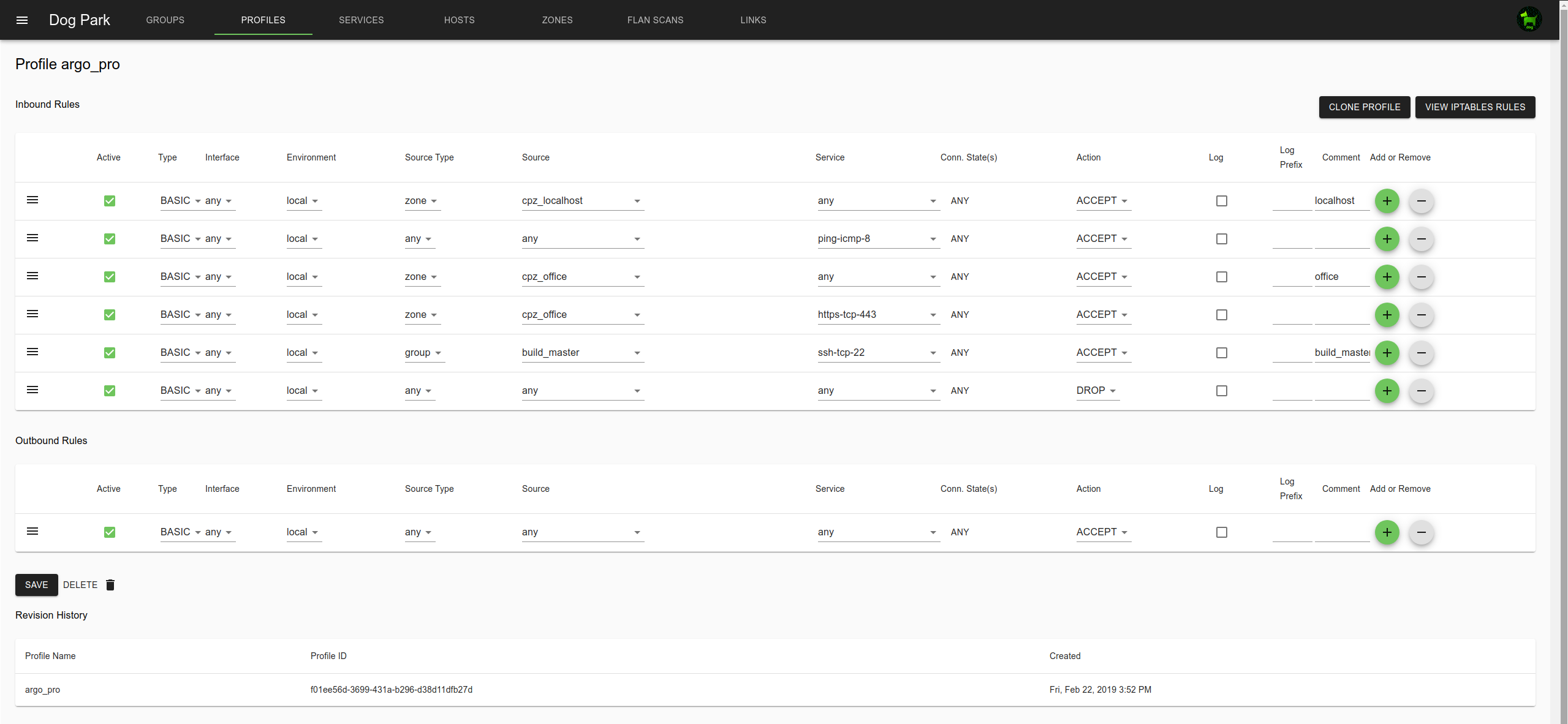
- Profiles are lists of Rules, and are assigned to Groups.
- Rules can include either Groups or Zones along with Services that describe the controlled protocols.
- Iptables are generated from these Rules and distributed to Agents.
- Ipsets are used to make fast, readable iptables rules even with thousands of addresses.
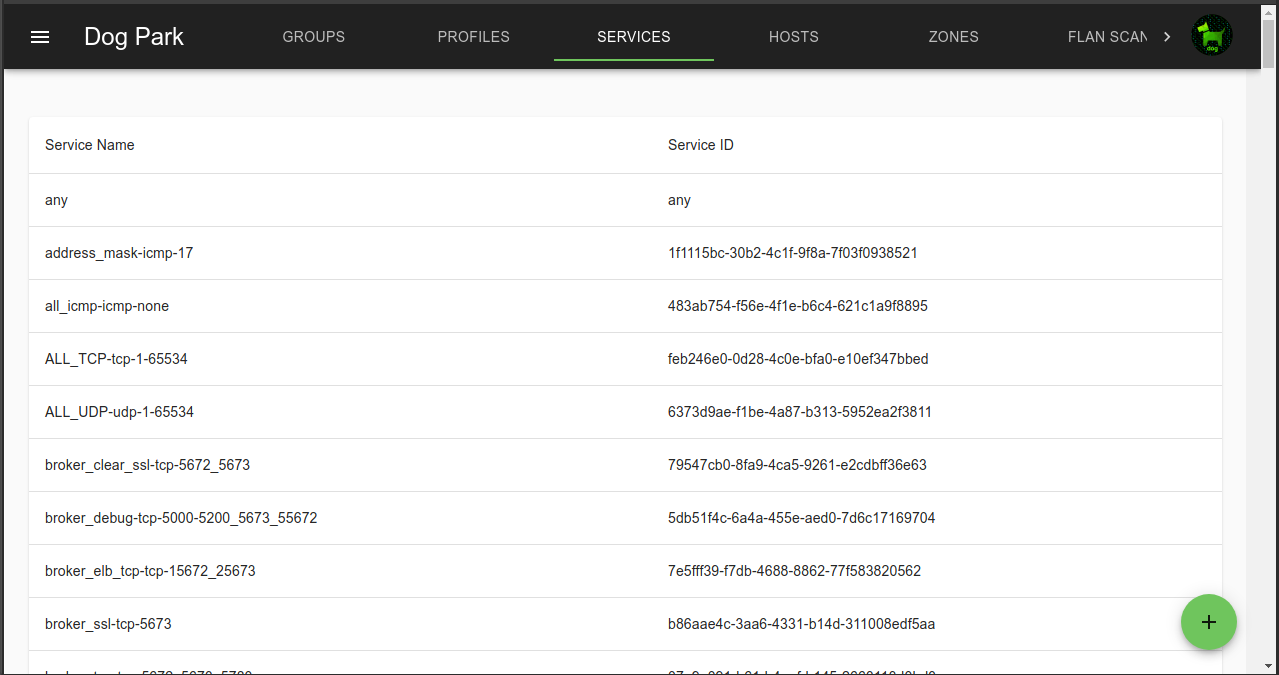
- Services define ports and protocols.
- Flan Scans show network vulnerabilities found on servers.
-
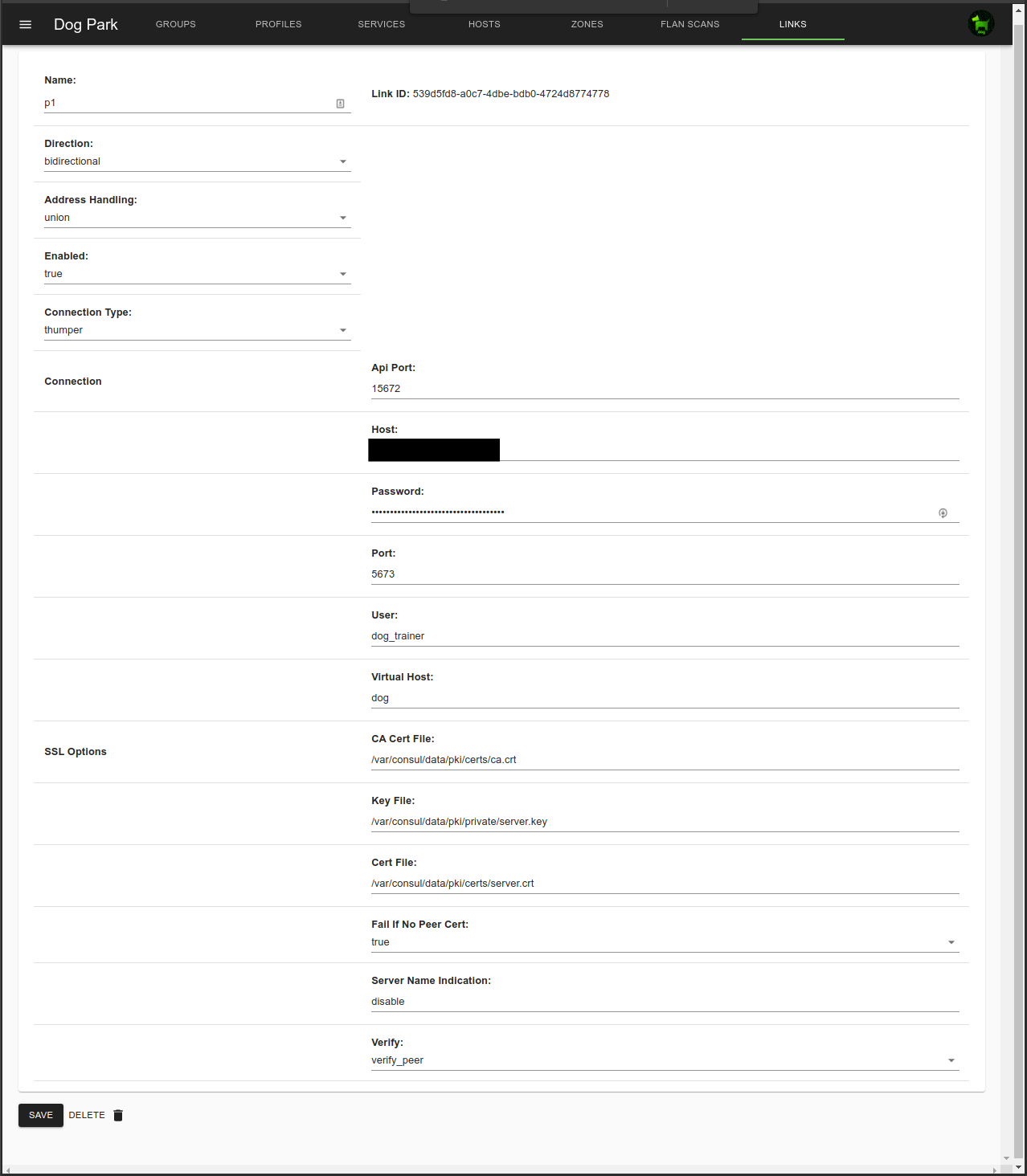
Links are used to share the addresses of Groups and Zones (as ipsets) between multiple dog_trainers.
- Configuration and runtime guides:
Web Console: dog_park
dog_park is the primary user interface for dog.
Hosts
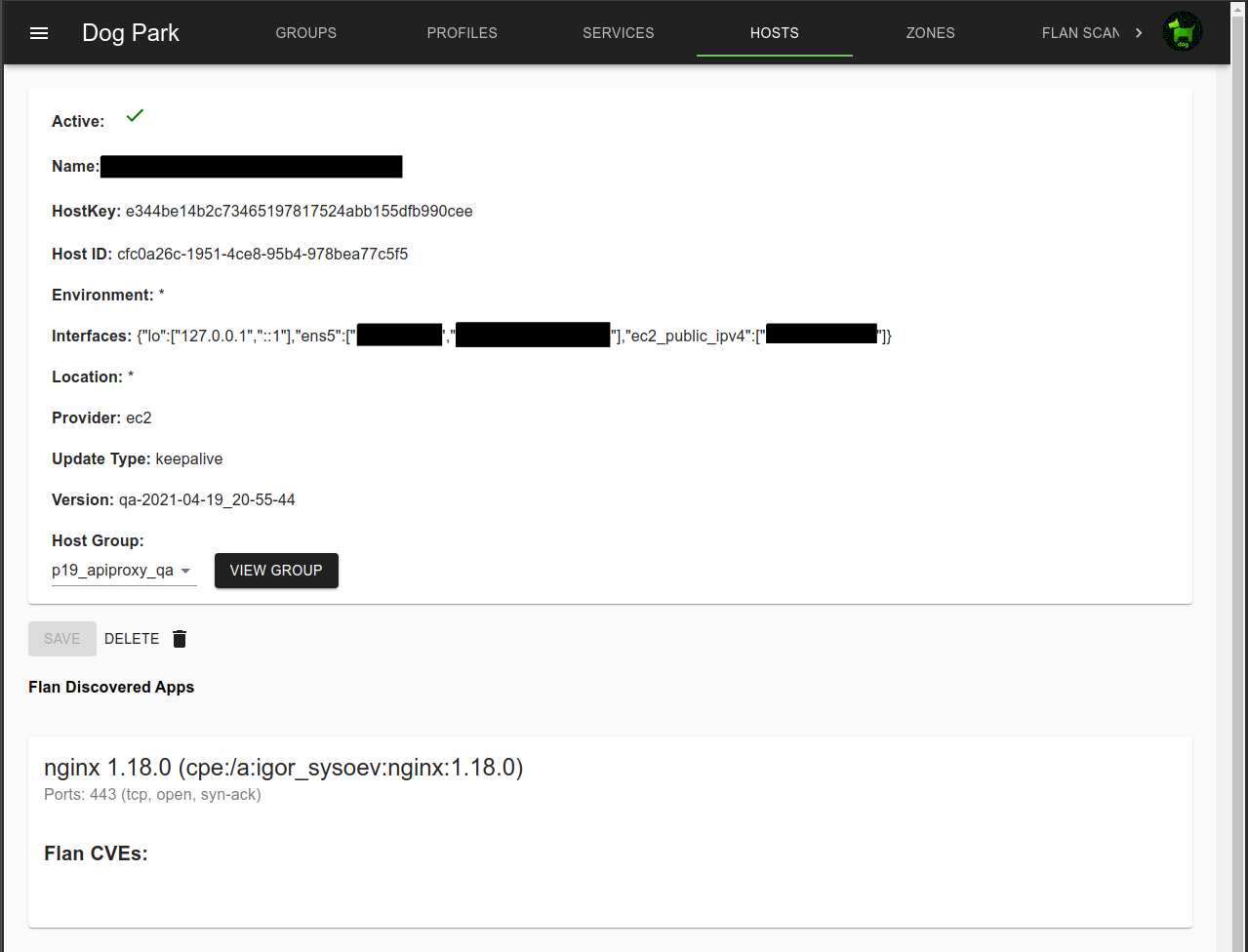
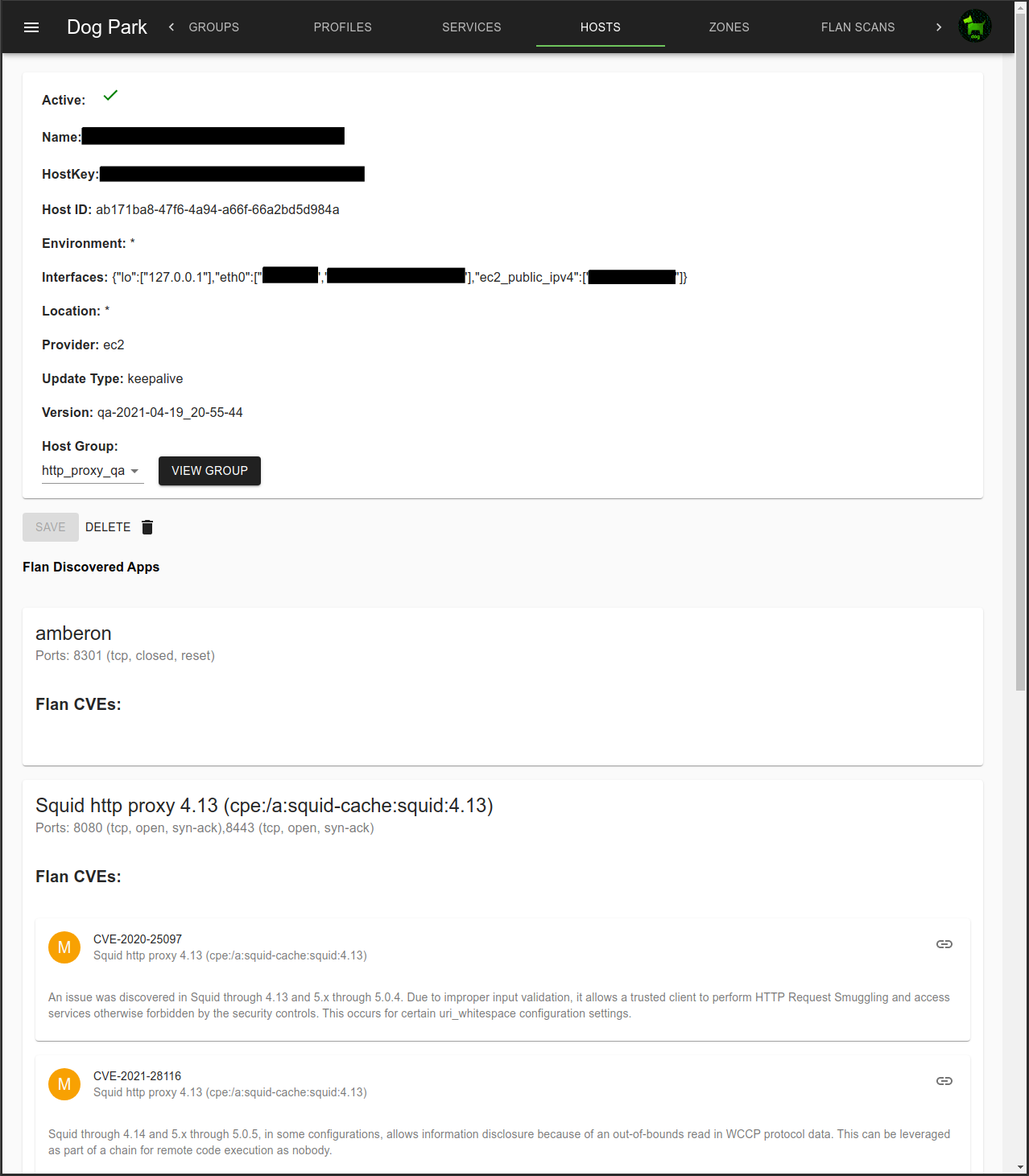
Each agent is listed in Hosts. Agents appear as Hosts as they attach to dog_trainer.
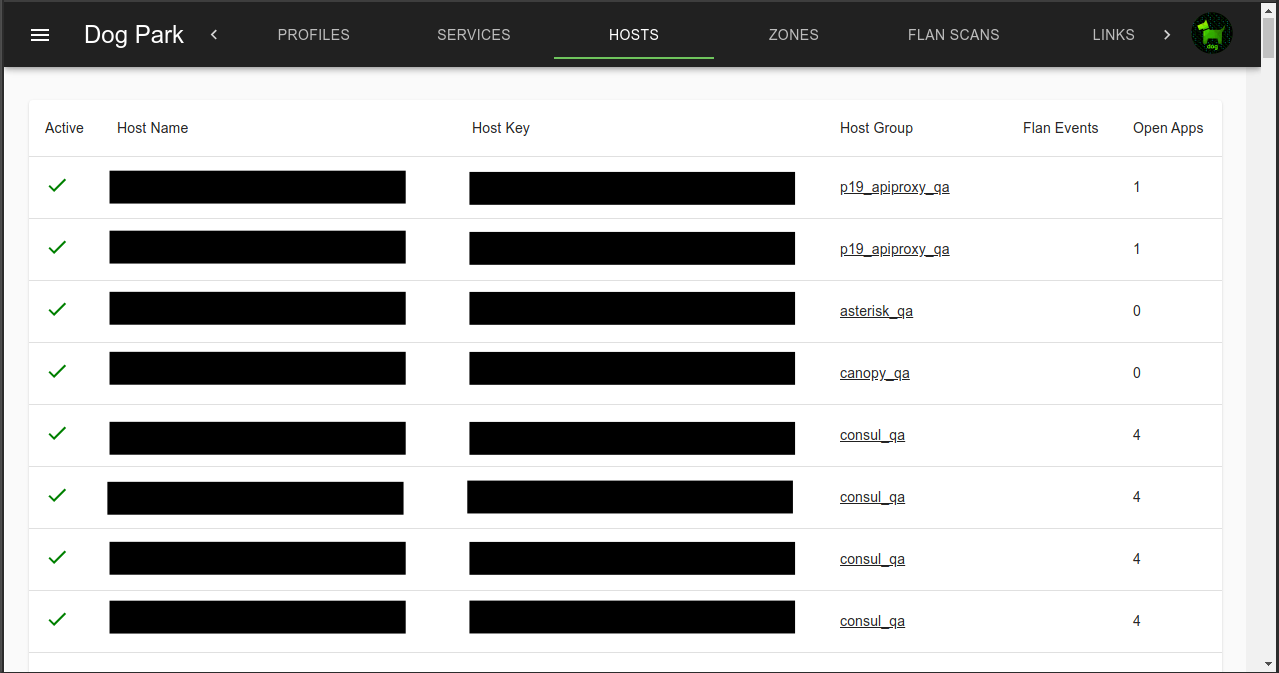
Hosts include local, public and ec2 public addresses.
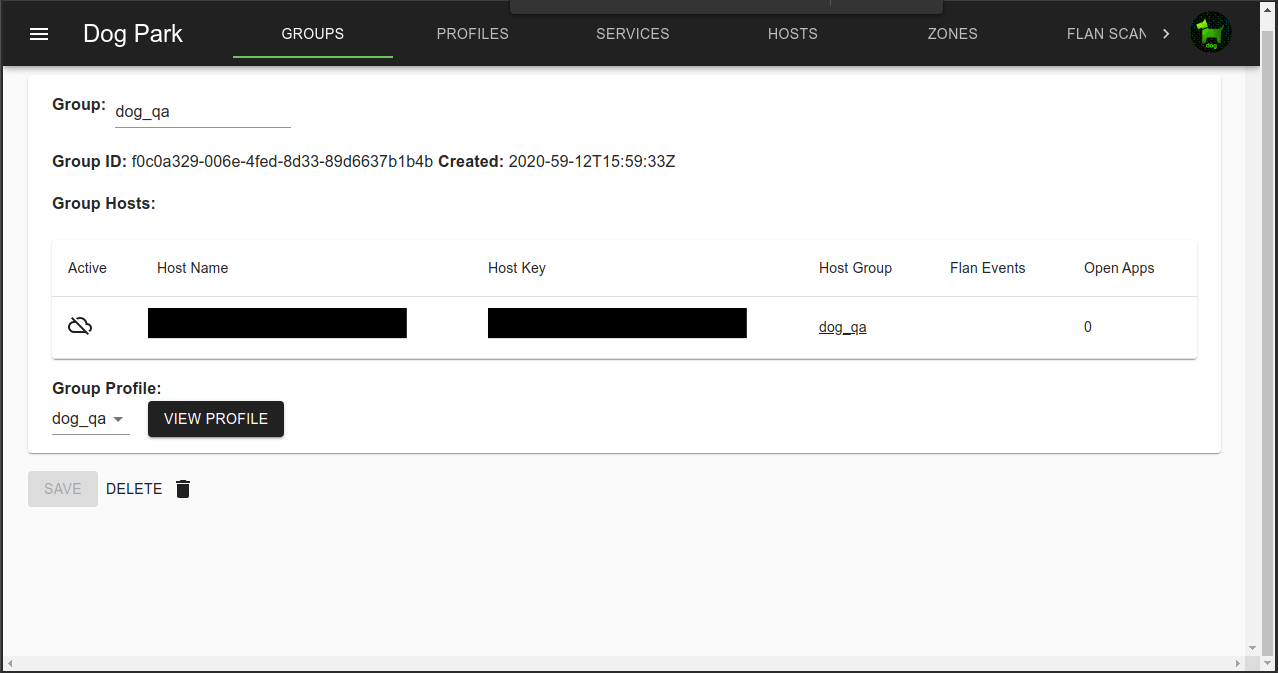
Groups
Hosts are assigned to a group, usually when the Agent is configured, but assignments can be changed in the console.
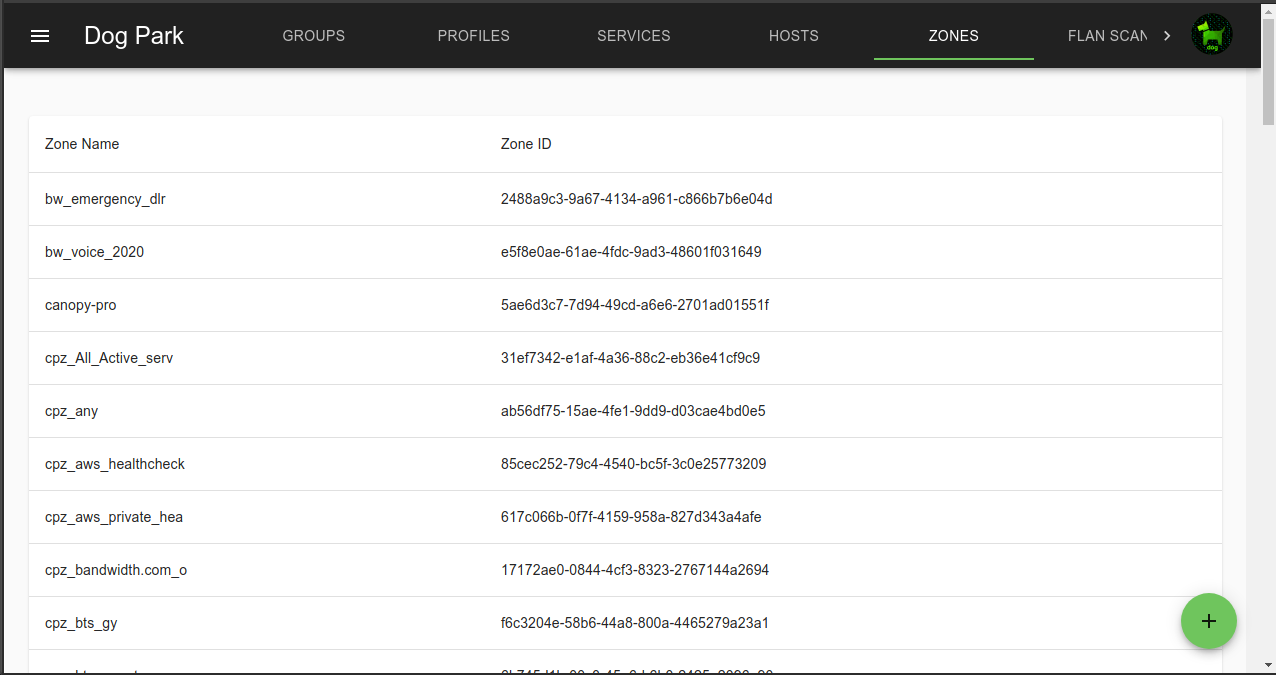
Zones
Zones are static lists of IPs that can be referenced in Profiles.
Fairly static Zones can be updated in the console, but highly dynamic Zones like block or allow lists can be modified via the dog_trainer API.
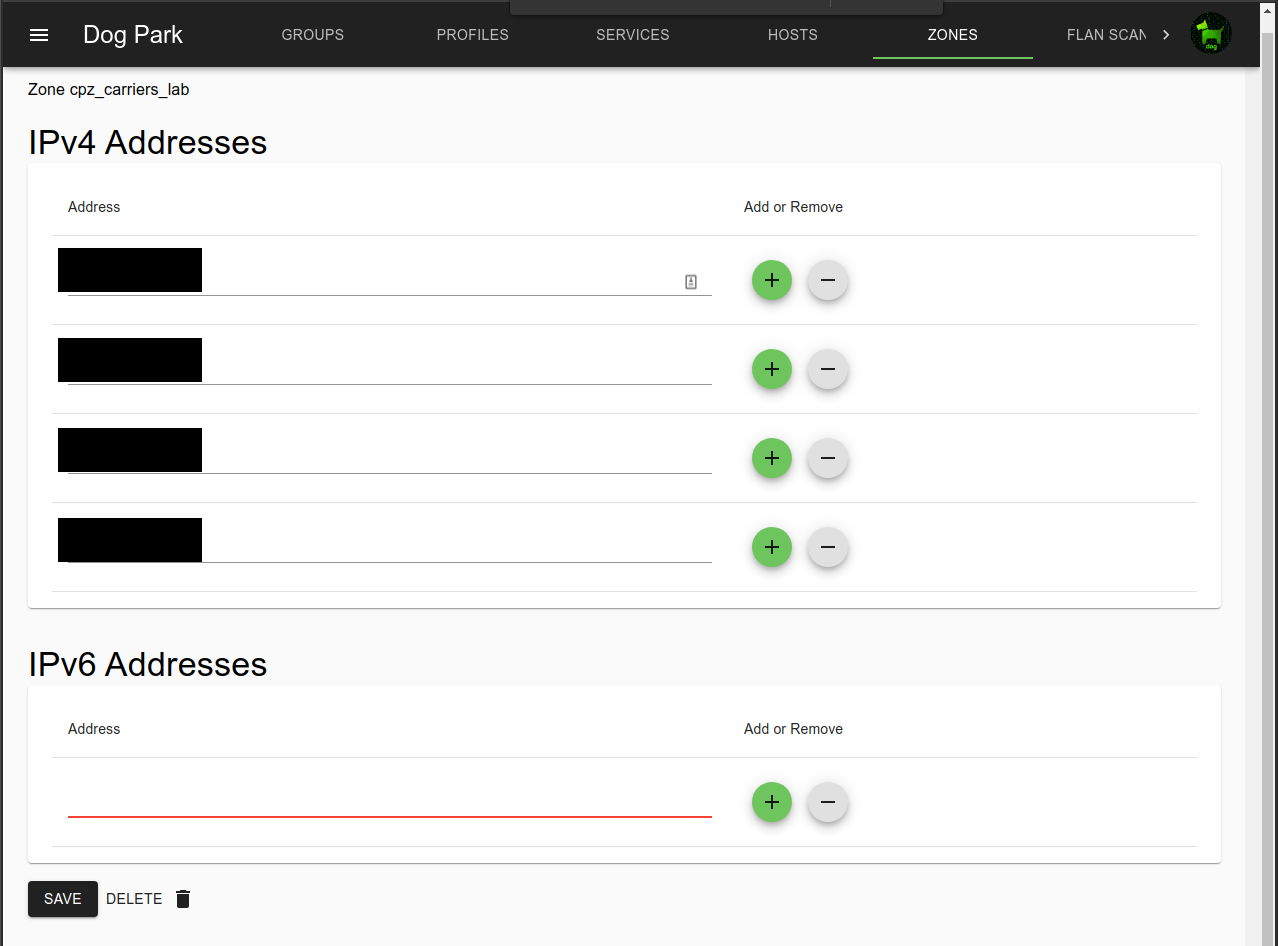
 Zones can include both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Zones can include both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Profiles
Profiles describe the access rules.
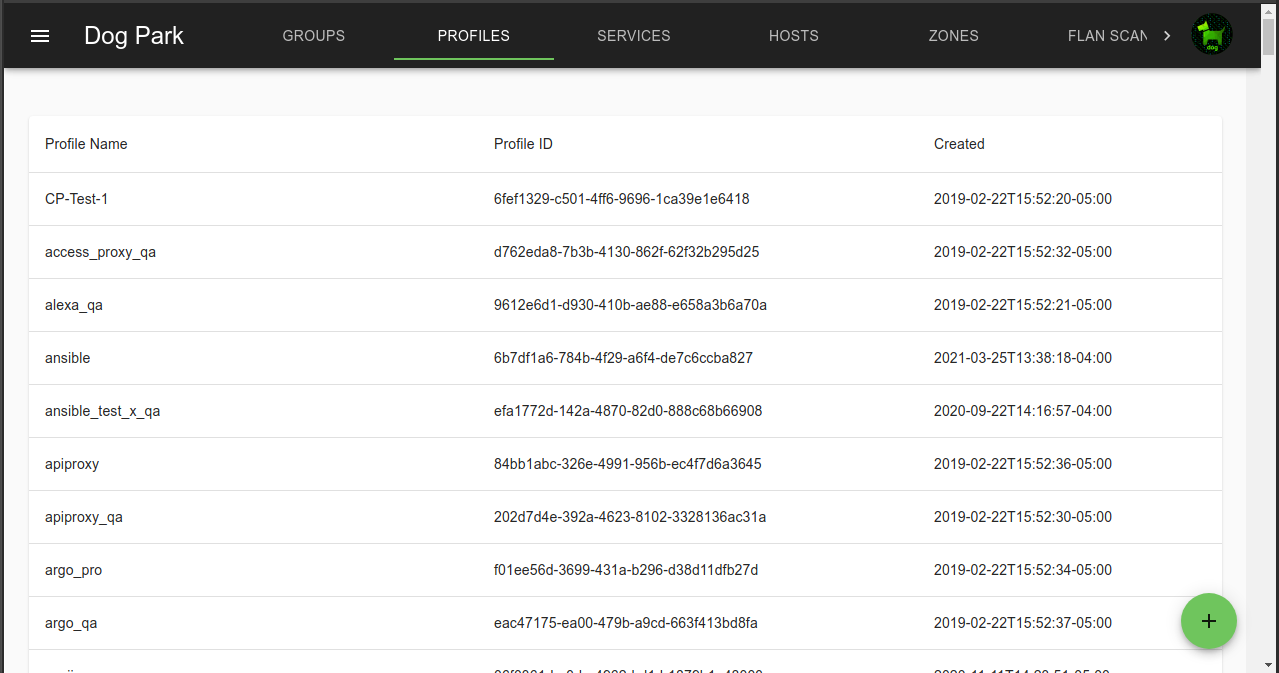
Group are associated with a Profile. Groups, Zones and Services are references in Profile rules.
Each rule can be active or inactive.
Rule types include: basic, connlimit (connection limit), recent (rate limit)
Source can be a Group or Zone.
Inbound tables are default DROP, so anything not specifically allowed by rules will be dropped.
Outbound tables are default ACCEPT.
Services
Ports and protocols are defines in Services.
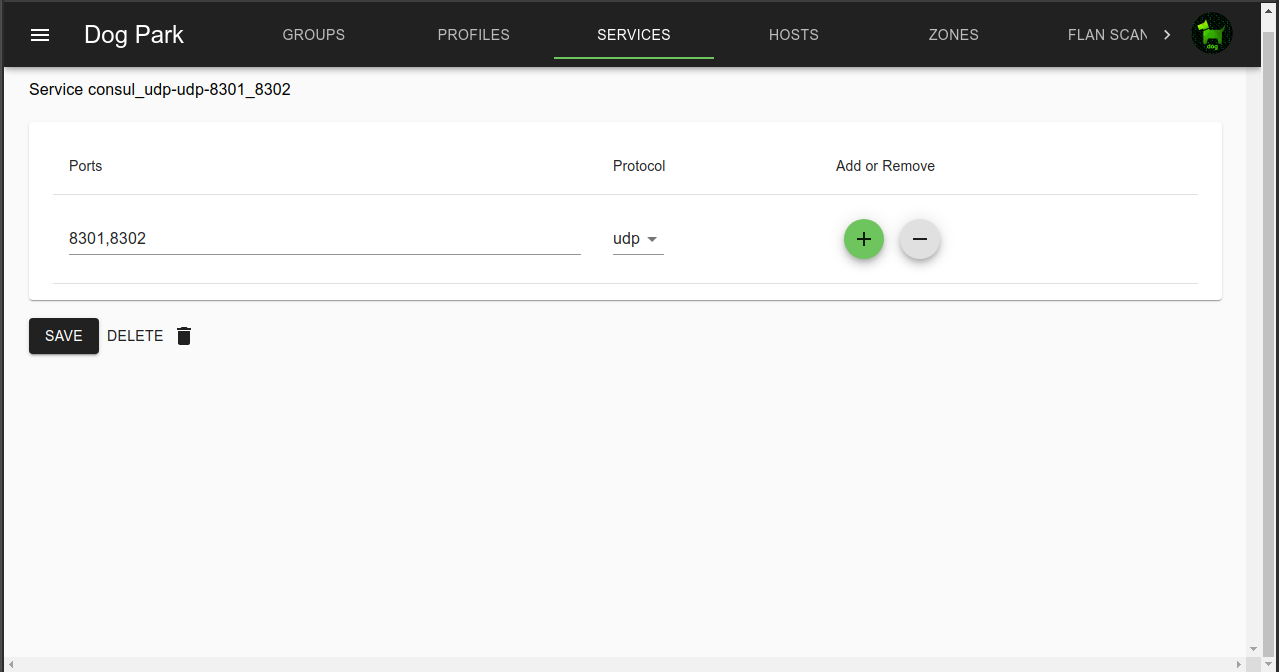
 Multiple ports, each with a different protocol types can be defined per service
Multiple ports, each with a different protocol types can be defined per service
Ports are delimited with commas
A range of ports is indicated with a “:” between start and end.
Flan Scans
Integration with the network vulnerability scanner Flan Scan is available.
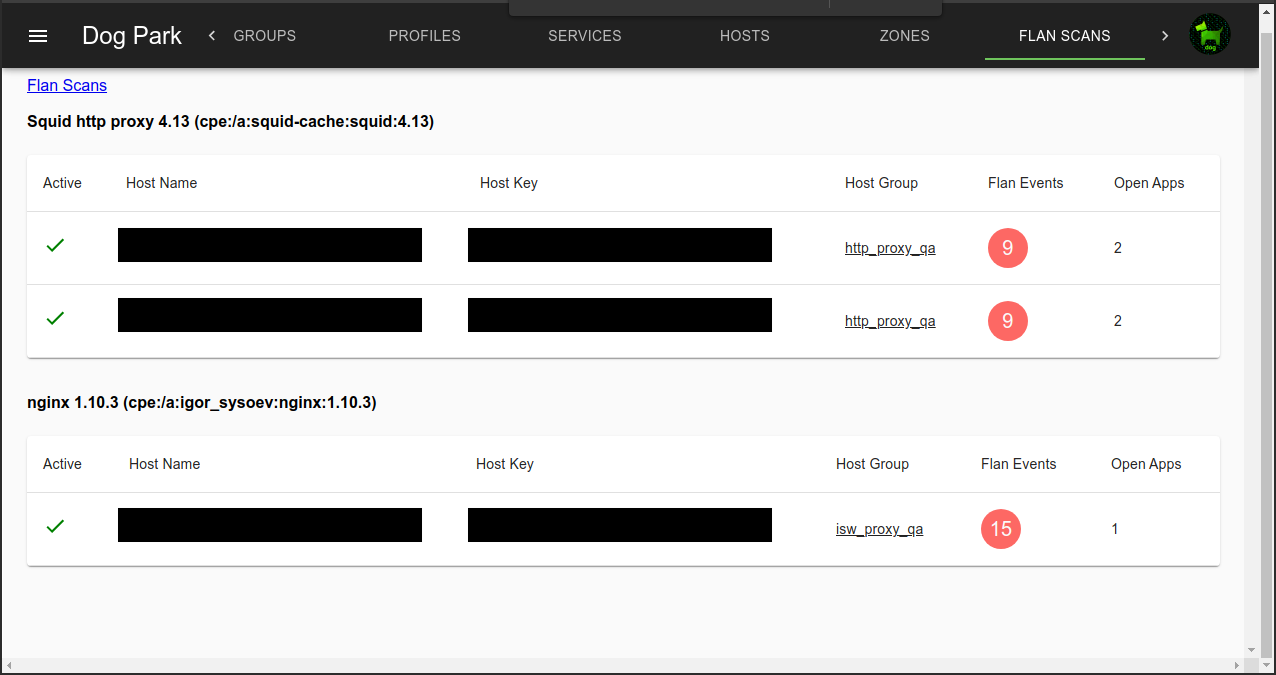 An example of a Host with a Flan Scan discovered CVE.
An example of a Host with a Flan Scan discovered CVE.
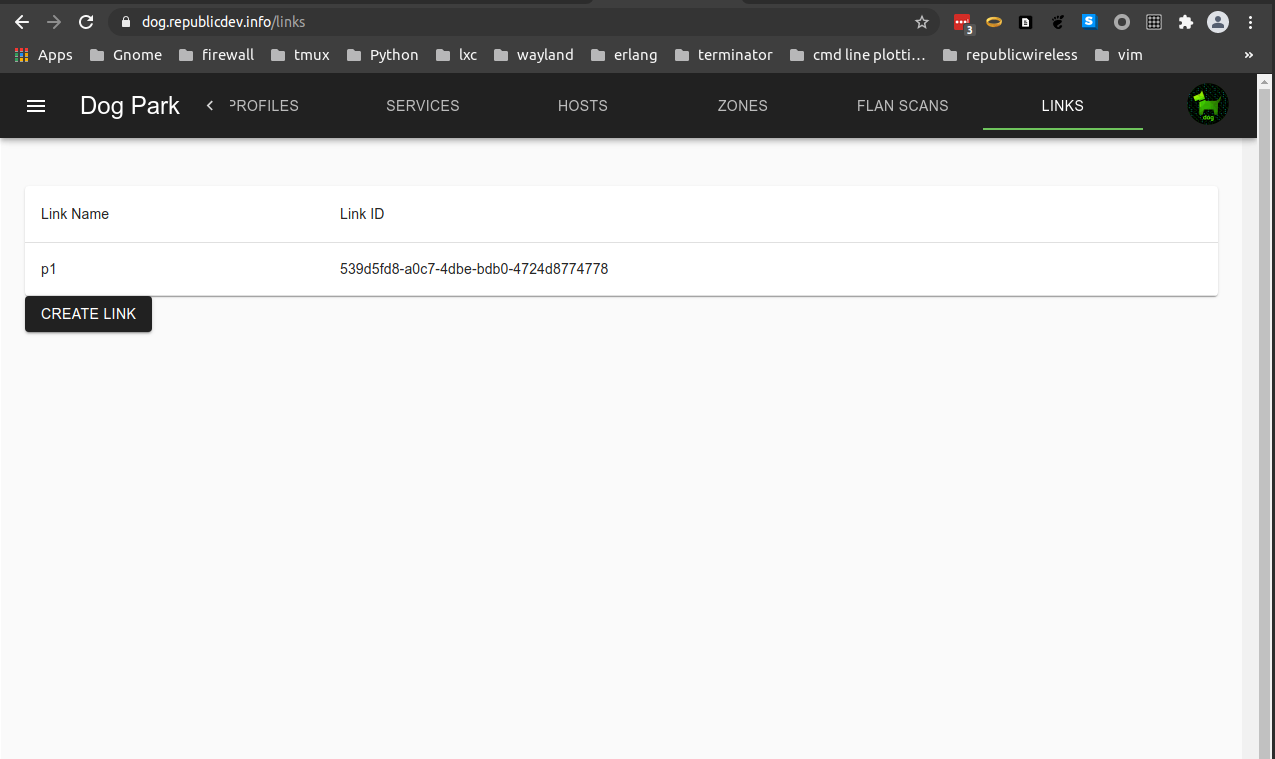
External Links
Links are the way to federate multiple dog_trainer instances.
Linked dog_trainers share Groups, Zones and Host addresses between dog_trainers, but not Profiles.
This is useful for sharing access between servers managed by different business units.
Direction can be bidirectional, inbound, or outbound.
- Bidirectional both sends and accepts addresses.
- Inbound only accepts addresses.
- Outbound only sends addresses.
Address Handling can be set to either Union or Prefix.
-
Union combines each dog_trainer’s host and zone addresses with the same name into the same ipset.
simplified example: A group called “web” in the “q1” and “p1” environments that have a Union link will combine the addresses of all Hosts in that group into a single ipset called “web” both environments.
This is useful for splitting a single environment up into multiple dog_trainers, for example between QA and Production environments.
-
Prefix creates unique ipsets for each host and zone in each environemt, adding the the two character link prefix to the ipset names to ensure they are unique.
simplified example: A group called “web” in the “q1” and “p1” environments that have a Prefix link will create two ipsets in each environment, one called “q1_web” and the other called “p1_web”.
Connection information is for the other sides’ RabbitMQ.